Image credit: Len Rubenstein
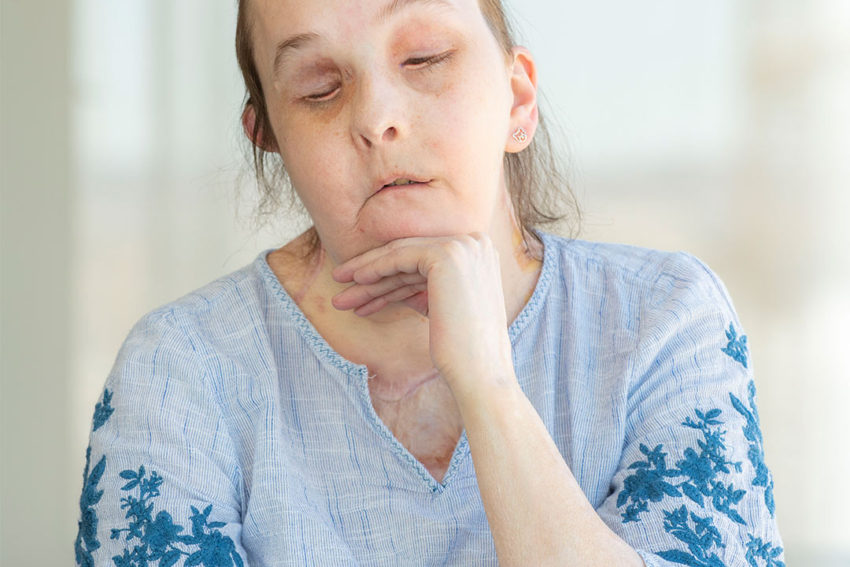
In 2007, Carmen Tarleton was attacked in bed by her ex-husband, who broke into the home where she lived with her daughters. He hit her with a baseball bat, then covered her face and body in industrial lye. Carmen’s injuries were so terrible that her doctors at Brigham and Women’s Hospital put her into a medically induced coma for three months.
Carmen underwent at least 55 separate surgeries before she was given a face transplant in 2013. She had also undergone multiple blood transfusions, and this exposure to other people’s blood made the rejection of her face transplant more likely. As a nurse for 20 years, Carmen was aware of the challenges of rejection, as she explained in an interview with the BBC. Her face transplant was widely reported, and she was interviewed for the BBC in 2015.
Asked what created her identity, Carmen replied that she had been a ‘disfigured person’ and a ‘person who had a new face’, and that the process had been strange and unsettling, though the ‘core’ of her identity unchanged. When she started dreaming again, which she did some months after the procedure, she began to dream about herself with her new face, suggesting some deep psychological acceptance.
In surgical terms, Carmen also made an exceptional recovery. CNN reported how she had ‘fulfilled her wish to kiss her boyfriend. She wrote a book, headlined an organ donor float in the Rose Parade, lectured about resilience, learned to play the banjo and became a hands-on grandmother’. Carmen Tarleton, speaking at the Congress of Future Medical Leaders in 2018 shared her secrets of resilience in an extraordinary and moving presentation.
There was no simple ‘before’ or ‘after’, however, between the ‘old’ and ‘new’ lives and faces, and this is a running theme of the work of the AboutFace project. As a society we tend to focus on transformations (of houses, landscape, weight, faces), but the reality is far more complex. Any long-term patient will experience multiple, often conflicting, emotional responses. Surgically and emotionally there will be successes and failures, good days and bad days. Like any transplant patient, moreover, Carmen lives with the day-to-day possibility of rejection; that her body would start to reject the organ she had received.
And rejection is something that all face transplant recipients will experience, albeit to different degrees. Unfortunately, for Carmen, this process became impossible to reverse. By 2019, parts of Carmen’s face began to die as its blood flow was restricted; she began to lose some of her transplanted hair and eyebrows, and part of her left nostril. Her surgeon Bohdan Pomahac and others at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston believed that the only option was another transplant, an even more challenging prospect than usual given the Covid-19 pandemic.
Carmen’s second face transplant made international headlines, just like the first. Some of those reported, incorrectly, that this was another surgical first: that there had never before been a retransplant. NBC News’ Today programme ran with the headline: ‘Domestic abuse survivor becomes 1st person ever to receive 2nd transplant.’
This is not the case, though Carmen’s second transplant was a first for the USA. In 2010 the French surgeon Laurent Lantieri performed the first face transplant on Jerome Hamon in 2010 in Paris; the second in 2015, after Hamon was given drugs that interfered with his anti-rejection medication.
Carmen’s second face transplant took place over two days, which is unusual; she needed to be stabilised in the ICU halfway through the surgery due to excessive bleeding, and so the face transplant was resumed the following day. Given the excessively long surgeries involved in face transplants, ranging from 20 to 30 hours, the fact that in this case the procedure was able to take place over two days put less pressure on the surgical team. This might even be a model for future face transplants, according to Dr Pomahac.
Carmen has met the family of her second face transplant recipient, just as she met the first. Her surgeon has told her that the transplant might only last for seven years, like the first, but Carmen is unconcerned about the future ‘I believe this face is going to last me until I leave the Earth’, she said in an interview to People magazine. ‘It is my last face. I won’t have a third’.
The success of Carmen’s second face transplant shows how far the procedure has come, in terms of managing immunosuppressants, surgical skills and expertise, and the preparedness of the public to conceive of face transplants as an acceptable form of transplantation. Carmen’s donor family was unsure, the second time round, whether donating their loved one’s face was something they could do. 36-year-old Casey Harrington had died of a drugs overdose, leaving behind a 15-year-old daughter. and the family was understandably grief-stricken.
Although Casey’s organs saved five more people, it was the idea of donating a face that was difficult for them emotionally. At least in the beginning. Researching the procedure, learning about its life-changing nature for other people, is what swayed their decision. The family and Carmen have since met online, and, after the lockdowns caused by Covid-19, they intend to meet in the flesh.
Raising the profile of face transplants in the media encourages people to donate the faces of their loved ones. But it also opens up a space for a public conversation about the challenges involved – physical, emotional and social – of the circumstances by which people end up as face transplant recipients or donors, and the multiple impacts of the surgery. The voices of patients like Carmen need to be heard if we want to understand the emotional and physical impacts of face transplants as a form of surgical innovation. This is why it is critical to move away from headlines that stress the competitive and revolutionary nature of face transplants (the drive to be ’the first’ having long dominated the history of medical innovation) towards a more patient- and person-centred understanding of face transplant.
By Fay Bound Alberti.
